Hebrides


The Hebrides (pronounced /ˈhɛbrɨdiːz/, HEB-ri-deez; Gaelic: Innse Gall) comprise a widespread and diverse archipelago off the west coast of Scotland. There are two main groups: the Inner and Outer Hebrides. These islands have a long history of occupation dating back to the Mesolithic and the culture of the residents has been affected by the successive influences of Celtic, Norse and English speaking peoples, which is reflected in the names given to the islands.[1]
Contents |
Geology and geography
The Hebrides have a diverse geology ranging in age from Precambrian strata that are amongst the oldest rocks in Europe to Tertiary igneous intrusions.[2][3][4]
The Hebrides can be divided into two main groups, separated from one another by The Minch to the north and the Sea of the Hebrides to the south. The Inner Hebrides lie closer to mainland Scotland and include Islay, Jura, Skye, Mull, Raasay, Staffa and the Small Isles. There are 36 inhabited islands in this group. The Outer Hebrides are a chain of more than 100 islands and small skerries located about 70 kilometres (43 mi) west of mainland Scotland. There are 15 inhabited islands in this archipelago. The main islands include Barra, Benbecula, Berneray, Harris, Lewis, North Uist, South Uist, and St Kilda.
A complication is that there are various descriptions of the scope of the Hebrides. The Collins Encyclopedia of Scotland describes the Inner Hebrides as lying "east of The Minch", which would include any and all offshore islands. There are various islands that lie in the sea lochs such as Eilean Bàn and Eilean Donan that might not ordinarily be described as "Hebridean" but no formal definitions exist.[5][6]
In the past the Outer Hebrides were often referred to as the Long Isle (Scottish Gaelic: An t-Eilean Fada). Today, they are also known as the Western Isles although this phrase can also be used to refer to the Hebrides in general.[Note 1]
The Hebrides are probably the best-known group of Scottish islands, but other groups include the islands of the Firth of Clyde, Islands of the Forth and the Northern Isles. The islands in the Clyde, especially Arran, are sometimes mistakenly called "Hebrides" too.
Language
The Hebrides contain the largest concentration of Scottish Gaelic speakers in Scotland. This is especially true of the Outer Hebrides, where the majority of people speak the language.[8] The Scottish Gaelic college, Sabhal Mòr Ostaig, is based on Skye and Islay.
Etymology
The first reference to a name similar to the modern Hebrides is by Ptolemy, who called the islands Αἱβοῦδαι = Haiboudai in Ancient Greek. Later texts in classical Latin, by writers such as Solinus, use the forms Hebudes and Hæbudes.[9]
The old Old Norse name, during the Viking occupation, was Suðreyjar,[10] which means "Southern Isles" (see also Sodor). It was given in contradistinction to Norðreyjar, or the "Northern Isles", i. e. Orkney and Shetland.
Ironically, given the status of the Western Isles as the last Gàidhlig speaking stronghold in Scotland, the Gaelic language name for the islands - Innse Gall - means "isles of the foreigners" which has roots in the time when they were under Norse occupation and colonisation, and in reference to the Norse-Gaels, known in Gaelic as the Gall-Ghaidhil (meaning Foreign Gaels).
History
Prehistory

The Hebrides were settled during the Mesolithic era around 6500 BC, after the climatic conditions improved enough to sustain human settlement.[11] There are many examples of structures from the Neolithic period, the finest example being the standing stones at Callanish, dating to the 3rd millennium BC.[12] Cladh Hallan, a Bronze Age settlement on South Uist is the only site in the UK where prehistoric mummies have been found.[13][14]
Celtic era
The earliest written mention of the Outer Hebrides was by Pomponius Mela, a Roman-Spanish geographer of the first century, who refers to a group of seven islands which he gave the name Haemodae. Pliny the Elder's Naturalis Historia of AD77 gives the name as Hebudes.[15] Other ancient writers such as the Egyptian astronomer Ptolemy mention the Hebrides, attesting to some contact of the peoples there to the Roman world. In 55 BC the Greek historian Diodorus Siculus wrote that there was an island called Hyperborea (which means "far to the north") where a round temple stood from which the moon appeared only a little distance above the earth every 19 years. This may have been a reference to the stone circle at Callanish.[16] A traveller called Demetrius of Tarsus related to Plutarch the tale of an expedition to the west coast of Scotland in or shortly before AD 83. He stated that it was a gloomy journey amongst uninhabited islands, but that he had visited one which was the retreat of holy men. He mentioned neither the druids nor the name of the island.[17]
Little is known of the history of the peoples of the Hebrides before the 6th century. The first detailed records of the islands comes with the arrival of St. Columba on Iona in the 6th century AD. It was this Irish-Scottish saint who first brought Christianity to the islands in the 6th century, founding several churches.
Norwegian control
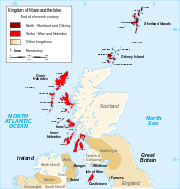
The Hebrides began to come under Norse control and settlement already before the 9th century. Norwegian rule of the Hebrides was formalised in 1098 when Edgar of Scotland recognised the claim of Magnus III of Norway. The Scottish acceptance of Magnus as King of the Isles came after the Norwegian king had conquered the Orkney Islands, the Hebrides and the Isle of Man in a swift campaign earlier the same year, directed against the local Norse leaders of the various islands. By capturing the islands Magnus imposed a more direct royal control over land seized by his kinsmen centuries earlier.
The Norwegian control of both the Inner and Outer Hebrides would see almost constant warfare until the partitioning of the Western Isles in 1156. The Outer Hebrides remained under the Kingdom of Mann and the Isles while the Inner Hebrides broke out under Somerled, the Norse-Gael kinsman of both Lulach and the Manx royal house.
After his victory of 1156 Somerled went on to seize control over the Isle of Man itself two years later and become the last King of Mann and the Isles to rule over all the islands the kingdom had once included. After Somerled's death in 1164 the rulers of Mann were no longer in control of the Inner Hebrides.
Scottish control
In 1262 there was a Scottish raid on Skye and this caused Haakon IV, King of Norway, to set sail for Scotland to settle the issue. Late in 1263 Haakon headed for Scotland with a large invasion force consisting of 200 ships and 15,000 men. The storms around the coast of Scotland took their toll on the Norwegian fleet, which at one point meant dragging forty ships overland to Loch Lomond. In the end a minor skirmish took place at the Battle of Largs where the Norwegians and their Manx allies under Magnus III of the Isle of Man failed to achieve anything against the Scots led by Alexander III, King of Scots. After the battle the bad weather forced the Norwegian-Manx fleet to sail back to Orkney. After arriving in Kirkwall, Haakon decided to winter in Bishop's Palace before resuming his campaign the following summer. This failed to occur as the king was struck by illness and died in his palace in December of the same year. The death of Haakon left the crown to his son Magnus the Lawmaker, who considered peace with the Scots more important than holding on to the Norwegian possessions off western Scotland and in the Irish Sea. The Treaty of Perth of 1266 left the Hebrides and the Isle of Man to Scotland for 4000 marks and an annual payment of 100 marks. The treaty also confirmed Norwegian sovereignty over Shetland and Orkney. Still, Scottish rule over the Isle of Man was confirmed finally only after the Manx and their last Norse king, Godred VI Magnuson were decisively defeated by the Scots in the 1275 Battle of Ronaldsway.
The arts

The Hebrides, also known as Fingal's Cave, is a famous overture written by Felix Mendelssohn while residing on these islands, while Granville Bantock wrote the Hebridean Symphony. Contemporary musicians associated with the islands include Ian Anderson, Donovan and Runrig. The poet Sorley MacLean was born on Raasay, the setting for his best known poem, Hallaig.[18] Iain Crichton Smith was brought up on Lewis and Derick Thomson was born there. The Hebrides are the setting of The Solitary Reaper, by William Wordsworth.
The novelist Compton Mackenzie lived on Barra and George Orwell wrote 1984 whilst living on Jura. J.M. Barrie's Marie Rose contains references to Harris inspired by a holiday visit to Amhuinnsuidhe Castle and he wrote a screenplay for the 1924 film adaptation of Peter Pan whilst on Eilean Shona.[19][20]
The poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow mentioned the Hebrides in his poem Seaweed.
The poet Edgar Allan Poe references the Hebrides in his poem The Valley of Unrest and in his short story Silence.
Enya's song "Ebudæ" from Shepherd Moons is named for the Inner Hebrides (Ebudae in Latin).
Virginia Woolf's novel To the Lighthouse is the story of a family's vacation house in the Hebrides (specifically, the Isle of Skye, part of the Inner Hebrides).
See also
- Outer Hebrides
- List of Outer Hebrides
- Inner Hebrides
- List of islands of Scotland
- Geology of Scotland
- Timeline of prehistoric Scotland
- Fauna of Scotland
- Somerled
- Kingdom of Mann and the Isles
- List of Kings of the Isle of Man and the Isles
- List of Kings of the Isle of Man
- Scottish Gaelic
- New Hebrides
References and footnotes
- General references
- "Occasional Paper No 10: Statistics for Inhabited Islands" (28 November 2003) General Register Office for Scotland. Edinburgh. Retrieved 15 September 2007.
- Haswell-Smith, Hamish. (2004) The Scottish Islands. Edinburgh. Canongate. ISBN 1-84195-454-3
- Keay, J. & Keay, J. (1994) Collins Encyclopaedia of Scotland. London. HarperCollins.
- Mac an Tàilleir, Iain (2003) Placenames/Ainmean-àite le buidheachas (pdf). Pàrlamaid na h-Alba. Retrieved 6 October 2009.
- Ordnance Survey (2009) "Get-a-map". Retrieved 1–15 August 2009.
- Ross, David (2005) Scotland - History of a Nation
- Murray, W.H. (1973) The Islands of Western Scotland. London. Eyre Methuen. ISBN 0413303802
- Notes
- ↑ Murray (1973) notes that "Western Isles" has tended to mean "Outer Hebrides" since the creation of the Na h-Eileanan an Iar or Western Isles parliamentary constituency in 1918. Murray also notes that "Gneiss Islands" – a reference to the underlying geology – is another name used to refer to the Outer Hebrides but that its use is "confined to books".[7]
- Citations
- ↑ Haswell-Smith, Hamish. (2004) The Scottish Islands. Edinburgh. Canongate. ISBN 1-84195-454-3
- ↑ Rollinson, Hugh (September 1997) " Britain's oldest rocks" Geology Today. 13 no.5 pp. 185-190.
- ↑ Gillen, Con (2003) Geology and landscapes of Scotland. Harpenden. Terra Publishing. Pages 44 and 142.
- ↑ Rollinson (1997) states that the oldest rocks in Europe have been found "near Gruinard Bay" on the Scottish mainland. Gillen (2003) p. 44 indicates the oldest rocks in Europe are found "in the Northwest Highlands and Outer Hebrides". McKirdy, Alan Gordon, John & Crofts, Roger (2007) Land of Mountain and Flood: The Geology and Landforms of Scotland. Edinburgh. Birlinn. p. 93 state of the Lewisian gneiss bedrock of much of the Outer Hebrides that "these rocks are amongst the oldest to be found anywhere on the planet". Other non-geological sources sometimes claim the rocks of Lewis and Harris are "the oldest in Britain", meaning that they are the oldest deposits of large bedrock. As Rollinson makes clear they are not the location of the oldest small outcrop.
- ↑ Keay & Keay (1994) p. 507.
- ↑ Encyclopædia Britannica (1978) states: Hebrides - group of islands of the west coast of Scotland extending in an arc between 55.35 and 58.30 N and 5.26 and 8.40 W." This includes Gigha, St Kilda and everything up to Cape Wrath – although not North Rona.
- ↑ Murray (1973) p. 32.
- ↑ Mac an Tàilleir, Iain (2004) 1901-2001 Gaelic in the Census (PowerPoint ) Linguae Celticae. Retrieved 1 June 2008.
- ↑ Louis DEROY & Marianne MULON, 1992, Dictionnaire de noms de lieux, Paris: Le Robert, article "Hébrides"
- ↑ Anderson, Joseph (Ed.) (1893) Orkneyinga Saga. Translated by Jón A. Hjaltalin & Gilbert Goudie. Edinburgh. James Thin and Mercat Press (1990 reprint). ISBN 0-901824-25-9
- ↑ Occupation at a site on Rùm is dated to 8590+/-95 uncorrected radiocarbon years BP. Edwards, Kevin J., and Mithen, Steven (Feb., 1995) "The Colonization of the Hebridean Islands of Western Scotland: Evidence from the Palynological and Archaeological Records," World Archaeology. 26. No. 3. p. 348. Retrieved 20 April 2008.
- ↑ Li, Martin (2005) Adventure Guide to Scotland. Hunter Publishing. p. 509.
- ↑ "Mummification in Bronze Age Britain" BBC History. Retrieved 11 February 2008.
- ↑ "The Prehistoric Village at Cladh Hallan". University of Sheffield. Retrieved 21 February 2008.
- ↑ [1] Scottish Gazetteer from the University of Edinburgh's Department of Geography.
- ↑ See for example Haycock, David Boyd. "Much Greater, Than Commonly Imagined." The Newton Project. Retrieved 14 March 2008.
- ↑ Moffat, Alistair (2005) Before Scotland: The Story of Scotland Before History. London. Thames & Hudson. pp. 239-40.
- ↑ Text of the poem in Gaelic, with Sorley Maclean's own translation into English Retrieved 2 June 2007.
- ↑ "Famous Visitors to the Islands - Luchd-tadhail Ainmeil" Culture Hebrides. Retrieved 26 July 2008.
- ↑ Birkin, Andrew, The Lost Boys. Yale University Press.
External links
|
||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
